News and Articles
-

Articles/Added: 24.03.2025
What is Carbon Sequestration and Why is it Important?
Carbon sequestration is the process of storing carbon in the soil through agricultural practices.Plants absorb CO₂ through photosynthesis and transform it into biomass, which eventually becomes part of the soil’s organic matter.This not only helps combat global warming but also improves soil structure, increases resilience to droughts and heavy rains, and enhances crop yields. Key Methods for Increasing Soil Carbon: Reducing mechanical soil tillage;Maintaining continuous plant cover (cover crops, perennial grasses);Integrating crop production and livestock farming;Applying organic fertilizers (manure, compost).…
To learn more -
Articles/Added: 13.08.2024
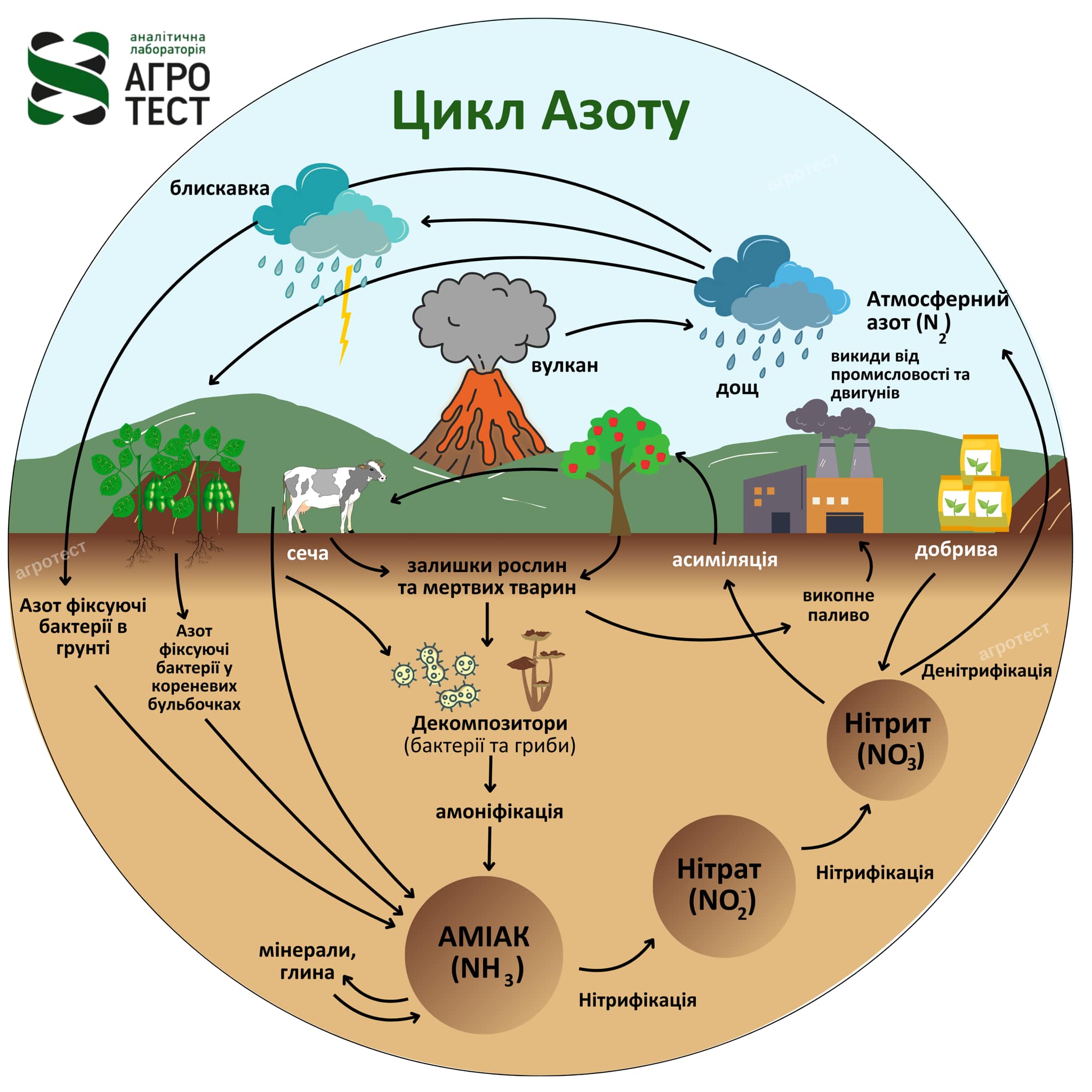
Nitrogen cycle and availability
Where does nitrogen come from? Nitrogen enters the soil through organic matter such as manure and plant residues.…
To learn more -
Articles/Added: 13.08.2024
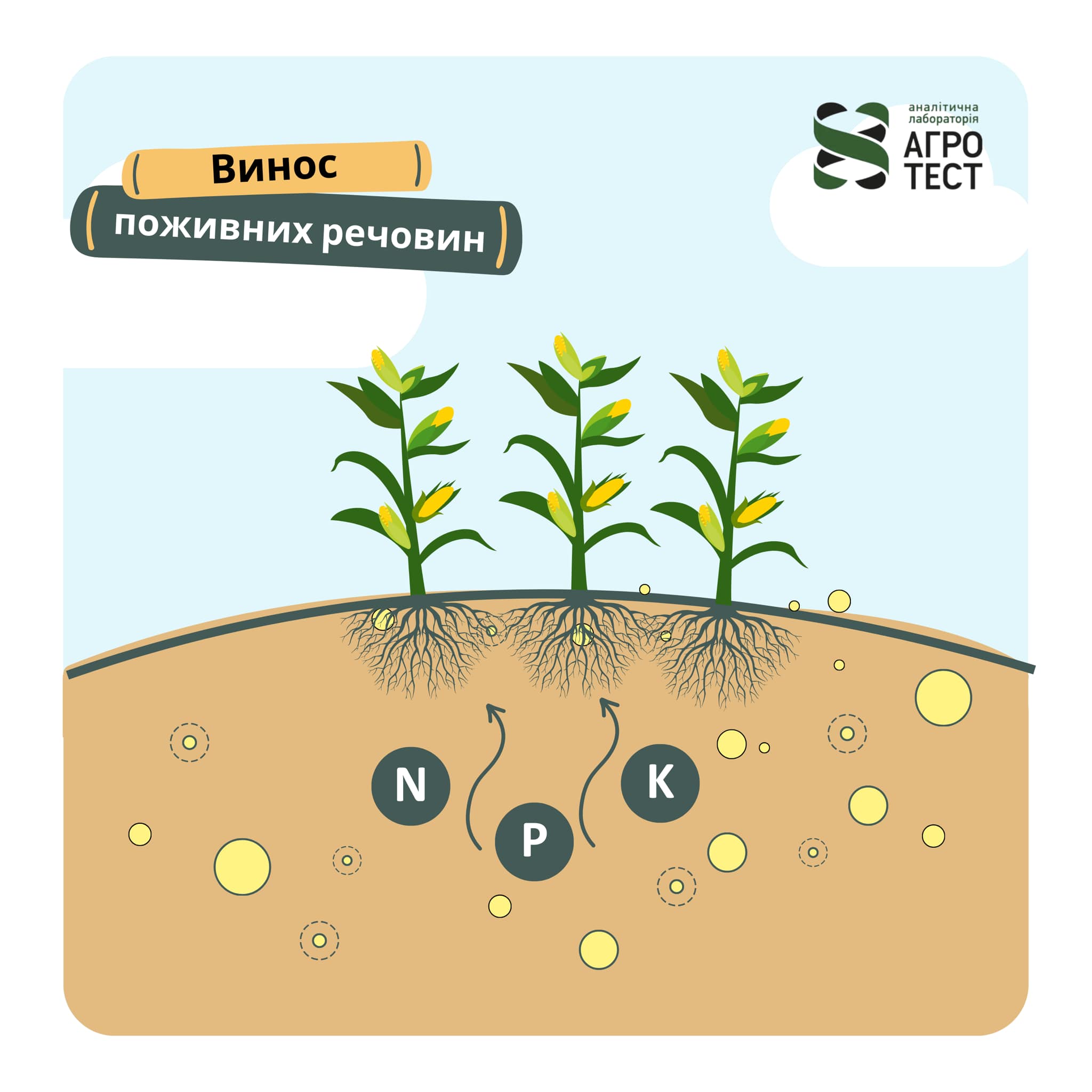
Removal of nutrients by crops
When we harvest, we not only get the product, but also deplete the soil of important nutrients! It's…
To learn more -
Articles/Added: 12.08.2024
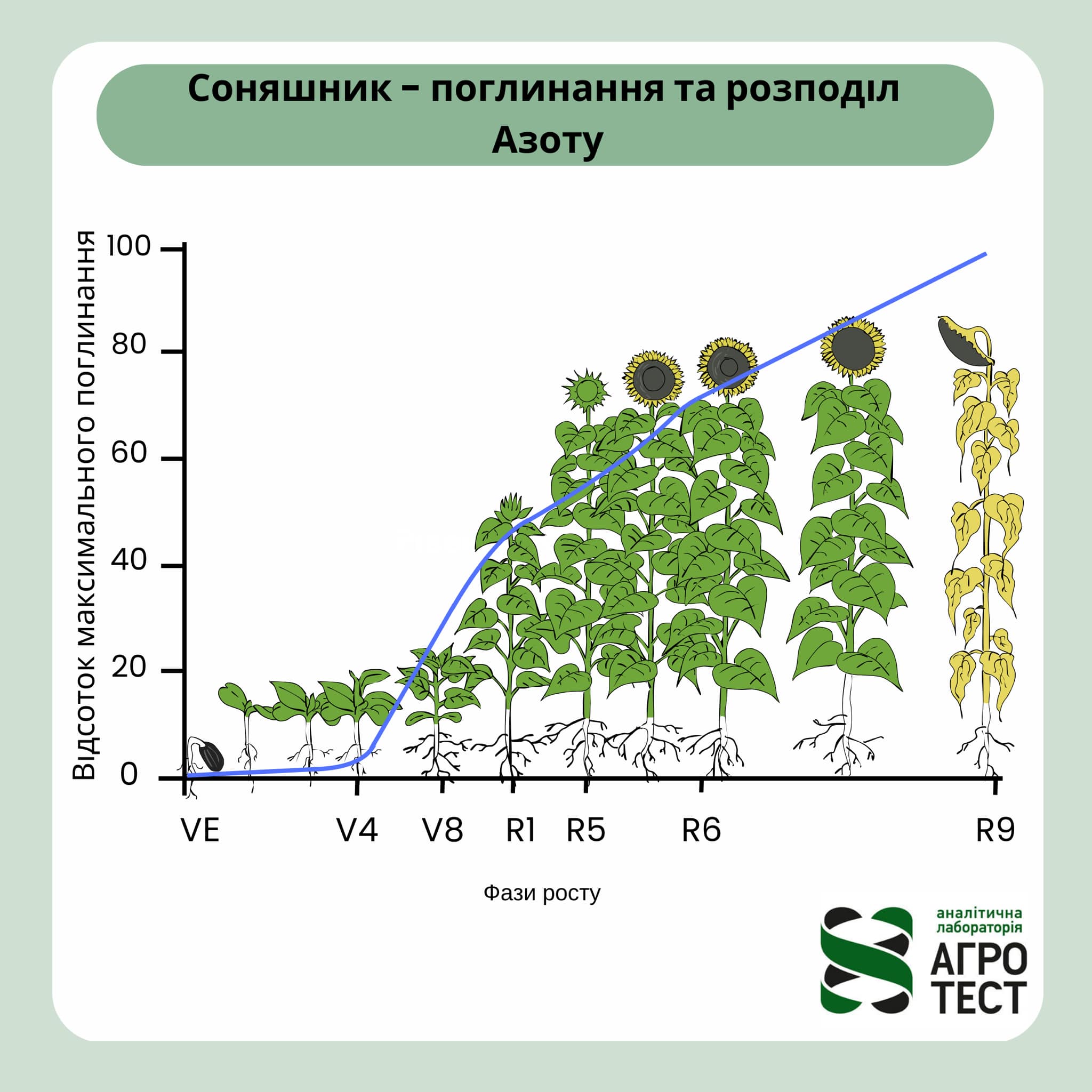
Nitrogen use by sunflower at different stages of growth
Let's look at the main stages of growth and the percentage of nitrogen consumption of the total consumption…
To learn more -
Articles/Added: 12.08.2024
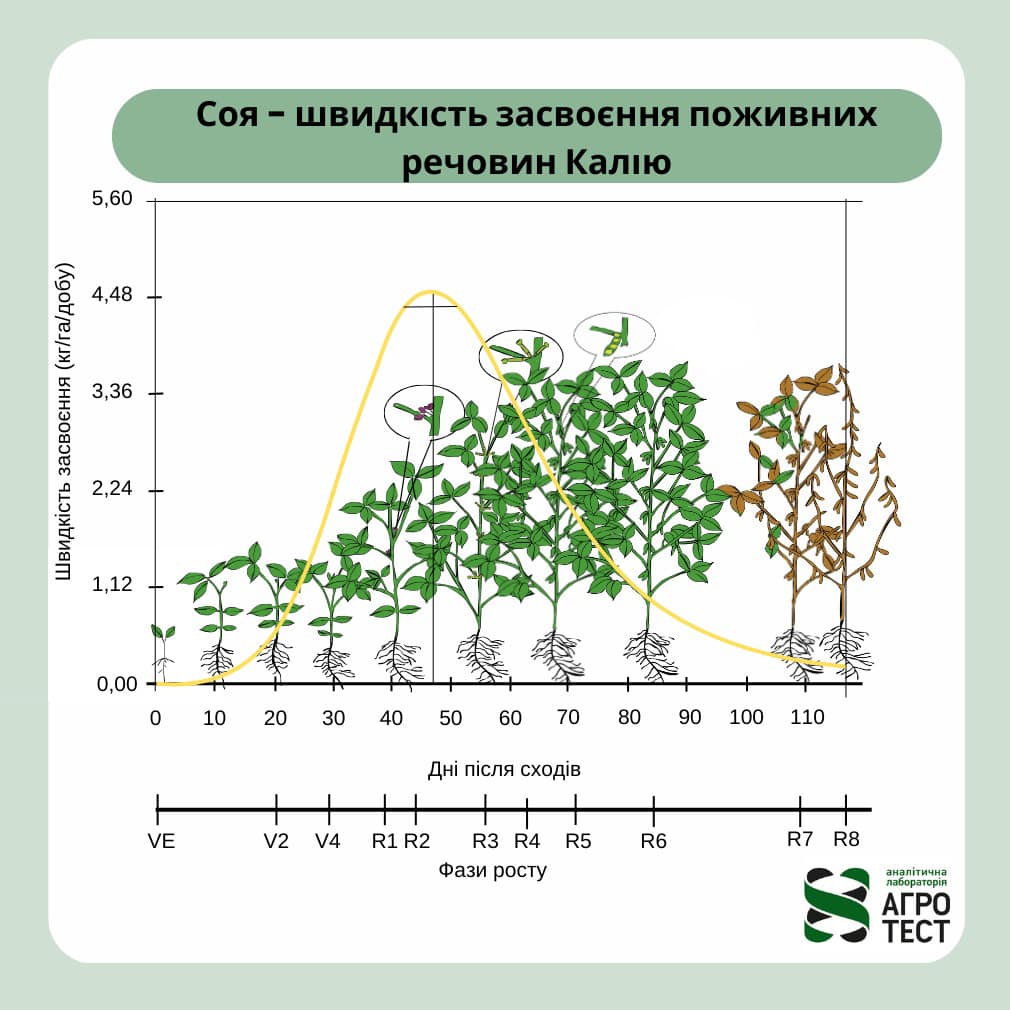
IMPORTANCE OF POTASSIUM FOR SOYBEANS
Soybeans require a significant amount of potassium: 2.4 kg of potassium (K2O) per 100 kg of grain. Vegetative…
To learn more -
Articles/Added: 12.08.2024
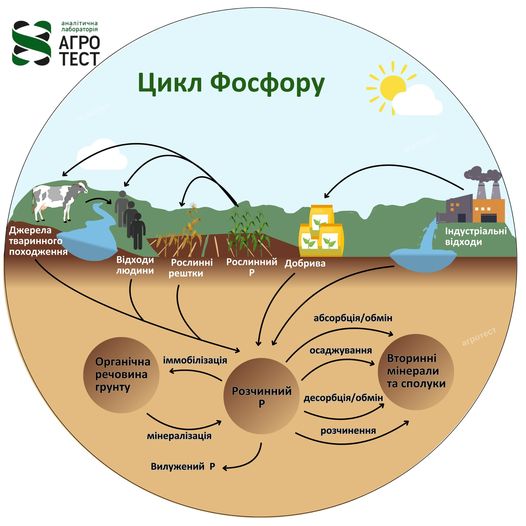
Influence of factors on phosphorus availability
In natural systems, phosphorus is present in the form of phosphates, which are formed when phosphorus reacts with air oxygen. The availability of phosphorus to plants depends on its condition in the soil. The state of phosphorus in the soil: 1) Fixed phosphorus: The largest pool of phosphorus in the soil that is not available to plants.It dissolves very slowly.It consists of insoluble inorganic phosphate compounds (primary minerals) and organic phosphorus compounds. 2) Active phosphorus: It is easily released and…
To learn more -
Articles/Added: 12.08.2024
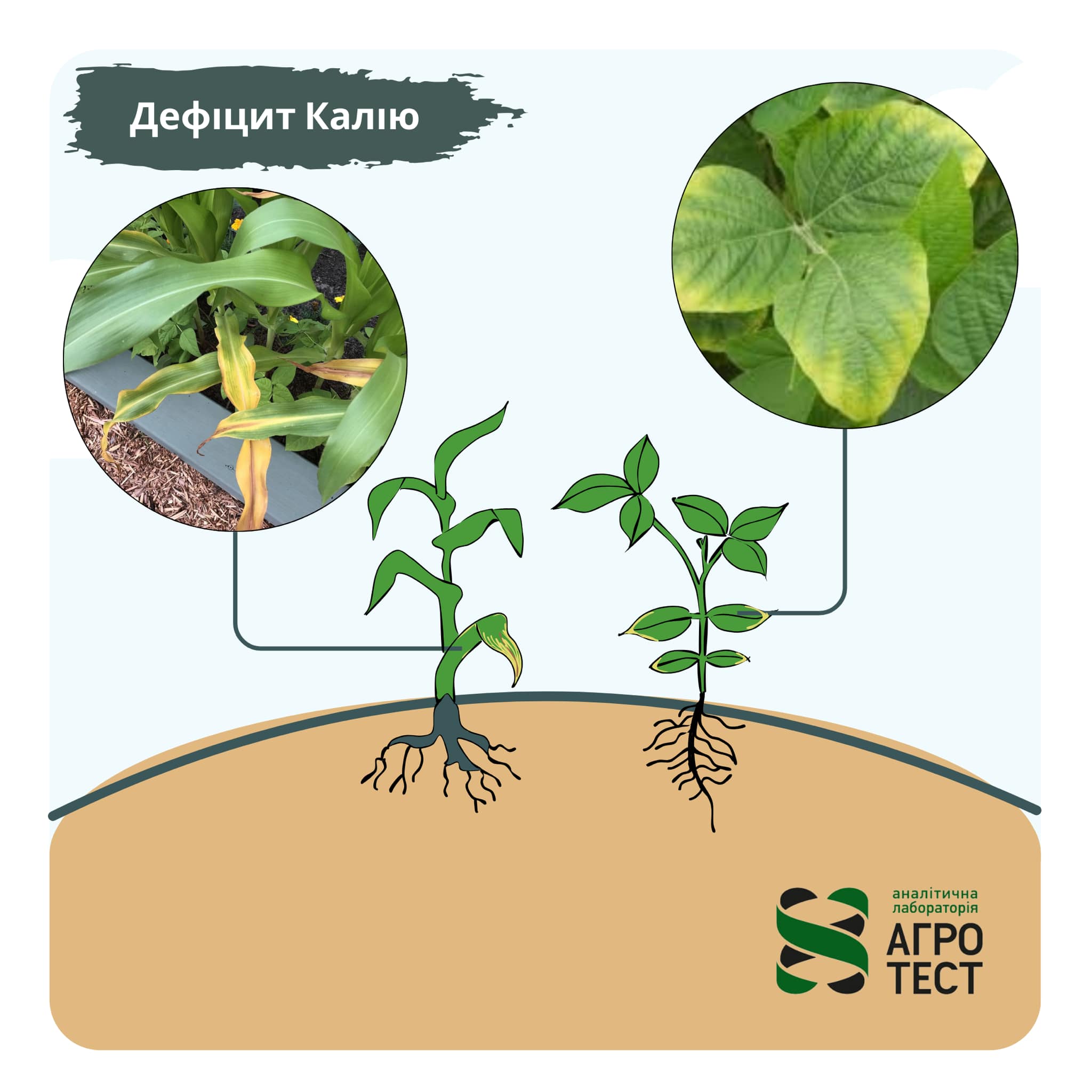
Corn and soybeans: signs of potassium deficiency
Corn: In maize, the edges of the lower leaves turn brown or yellow. This is accompanied by a…
To learn more -
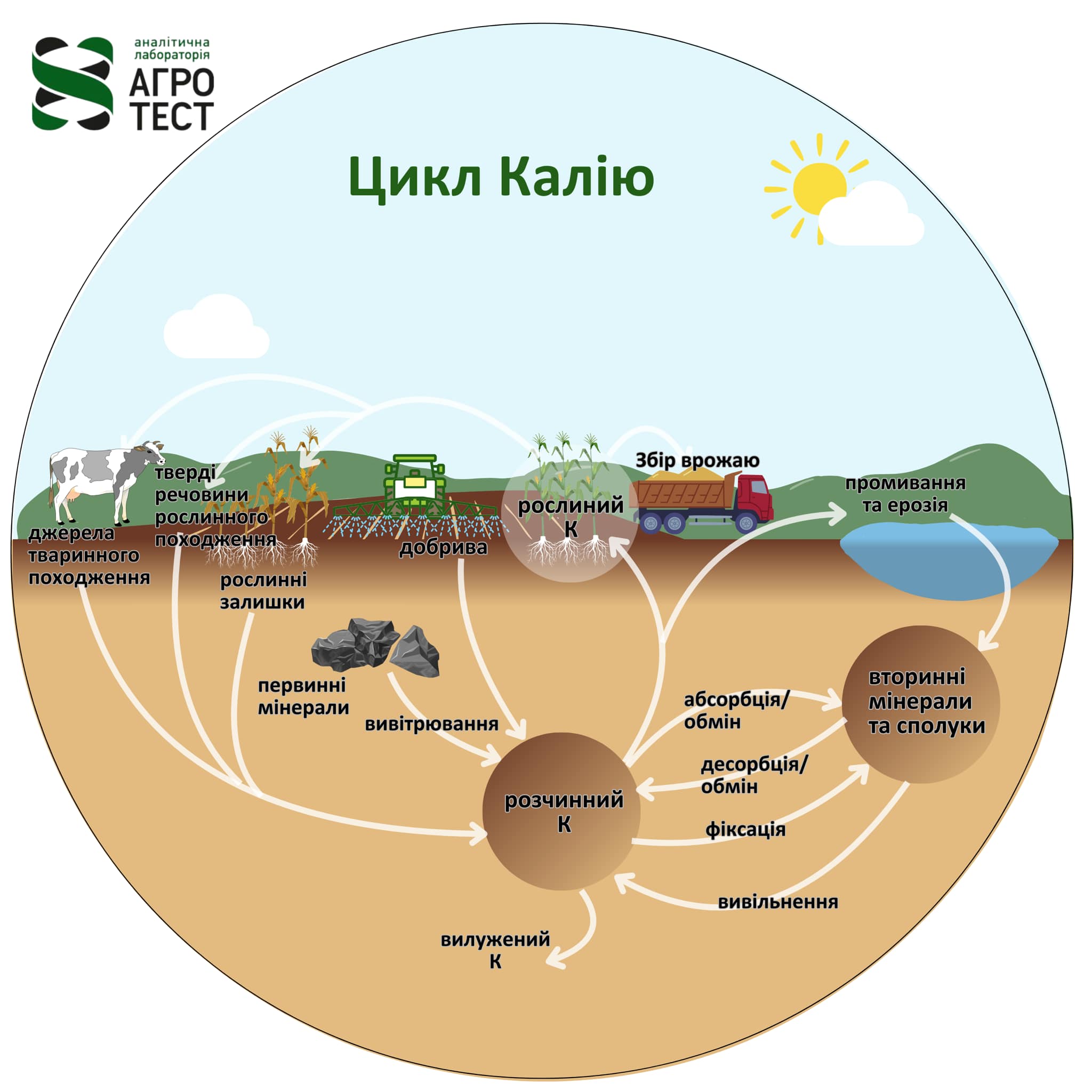

Articles/Added: 02.08.2024
Factors influencing potassium availability
Did you know that most potassium in soil is not available to plants? In this article, we will…
To learn more -
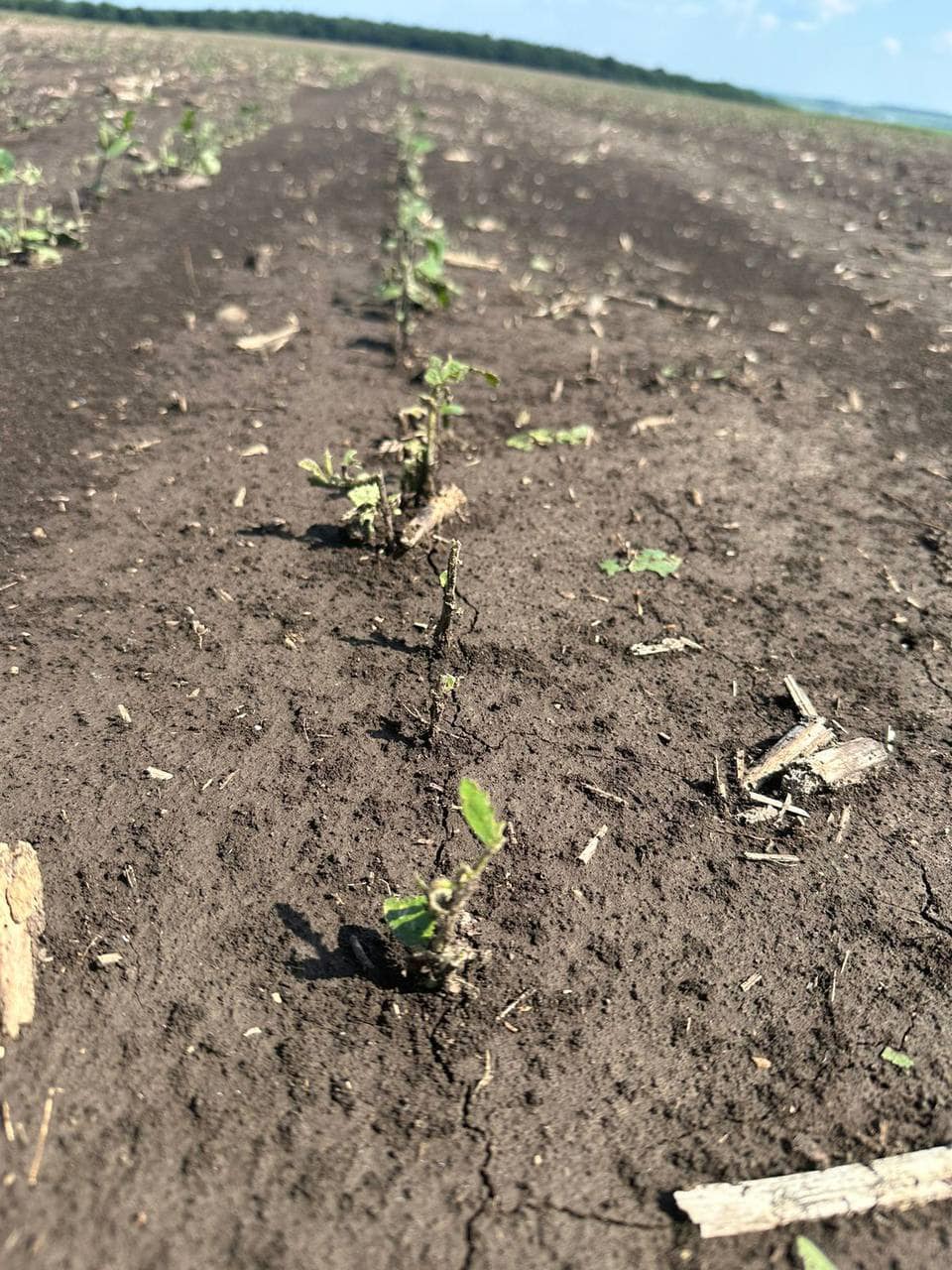

Articles/Added: 02.08.2024
The impact of hail on the soybean crop
Recently, many regions of Ukraine experienced heavy hail, which caused significant damage to soybean crops. In such circumstances,…
To learn more -

Articles/Added: 02.08.2024
Phosphorus deficiency in plants: how to identify it?
Symptoms of phosphorus (P) deficiency in plants can be subtle. Most often it is a reduction in plant…
To learn more -
Articles/Added: 01.08.2024
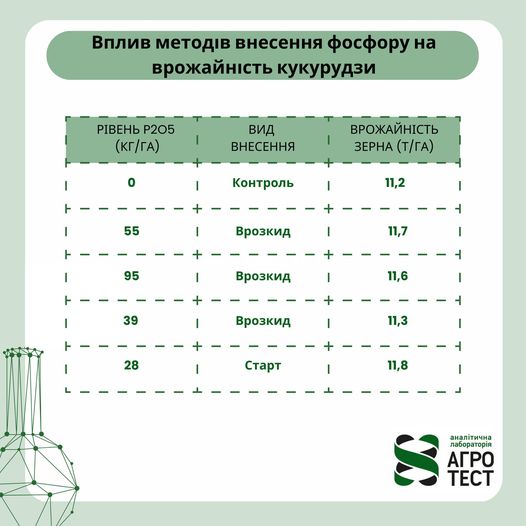
Belt fertilizer application versus spreading
Spreading phosphorus application This is the traditional method of spreading phosphorus evenly over the entire field. It has its advantages: Simplicity and speed of application.Suitable for large areas. But there are also disadvantages: Phosphorus may not reach the root system of plants.Fertilizer costs can be higher because some phosphorus is not used efficiently. Belt application of phosphorus This method involves applying phosphorus directly to the soil next to the seeds (5 cm to the side and below the seeds). Advantages…
To learn more -
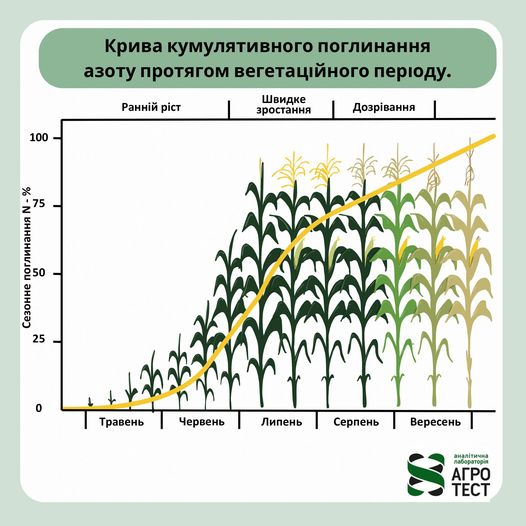
Articles/Added: 01.08.2024
How corn absorbs Nitrogen during the growing season
Stages of nitrogen absorption: Initial Phase (V1-V6): At the very beginning of the growing season, when corn is…
To learn more -

Articles/Added: 28.05.2024
Phosphate fertilisers: An energy boost for your plants
Phosphate fertilisers have the unique ability to quickly give plants an "energy boost", which makes them indispensable during…
To learn more -

Articles/Added: 28.05.2024
How and when do I use foliar fertilisers?
Foliar fertilisers are an effective way to give your plants an extra boost of nutrients. Here are some…
To learn more -

Articles/Added: 28.05.2024
Soil salinity: The invisible threat to your field
Did you know that soil salinity can be a serious obstacle to growing plants? What is soil salinity?…
To learn more
Questions that interest you
-
HOW TO SEND SOIL AND PLANT SAMPLES TO US IN THE LABORATORY?
You can send the sampled soil and plant samples to our laboratory by any courier convenient for you, which is in your locality. Recipient: Agrotest Analytical Laboratory, Stolychne Shosse 100, Kyiv.
-
WHERE TO SEE EXAMPLES OF RESULTS
Example of the results of soil analysis - see here
Example of plant analysis results - see here
Example of analysis results for the service "precision farming" - see here
-
WHAT ADDITIONAL INFORMATION IS REQUIRED TO RECEIVE RECOMMENDATIONS?
For a standard laboratory analysis, you need to know the planned yield of three different crops (if you do not clearly understand the crop to be grown next season) or one crop with three different yield options (if the crop is clear but the grower wants to compare costs for each planned yield). Any additional information will also be useful, such as information on the presence or absence of irrigation, rainfall in the region where the fields are located, last year's predecessor crops and their yields, and more.
-
WHAT SHOULD I DO IF THE PLANTS IN ONE AREA OF MY FIELD LOOK GREEN AND HEALTHY, BUT IN ANOTHER?
For comparative analysis, we recommend that plant samples be taken from each of these sites. It is also useful to include in the comments all information about management practices in these areas (if there were any differences). After harvesting, soil samples are also recommended to be taken separately from each plot.
-
DO I HAVE TO PAY SEPARATELY FOR RECOMMENDATIONS?
No, because the fee for recommendations is included in the total cost of conducting a full comprehensive agrochemical analysis.
-
IS IT POSSIBLE TO DOWNLOAD THE SOIL TEST RESULTS FOR ACCURATE AGRICULTURE TO THE CLIENT'S SOFTWARE
Yes! At the client's request, Agrotest Analytical Laboratory can give the results of soil analysis for precision farming in many well-known modern formats used by all modern manufacturers of precision farming equipment.
Write to us
and we will find an opportunity
for cooperation