Let’s read soil analysis results
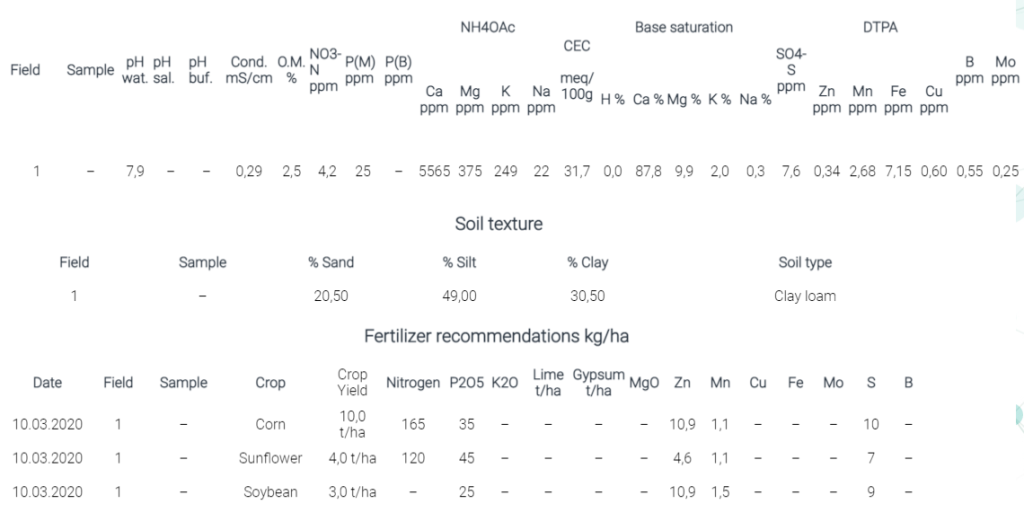
Soil pH (7.9) is alkaline.
Soil salinity (Сond = 0.29) is within optimal values.
Soil organic matter level (OM = 2.5) refers to average values.
The available phosphorus (P = 25 ppm) and exchangeable potassium (K = 249 ppm) are within the mean values (P) and very high values (K).
The values of the exchangeable forms of calcium (Ca = 5565 ppm) and magnesium (Mg = 375 ppm) are within high values.
Microelements such as: copper (Cu = 0.6 ppm), iron (Fe = 7.15 ppm), molybdenum (Mo = 0.25 ppm) and boron (B = 0.55 ppm) indicate their complete suitability for the specified crops and planned yield. Zinc (Zn = 0.34 ppm), manganese (Mn = 2.68 ppm) and sulfur (S = 7.6 ppm) are in low level.
Sulfur deficiency can be eliminated by introducing ammonium sulfate (NH4)2SO4; dose of ammonium sulfate kg / ha = Sulfur x 5.
On maize in the 9-10 leaf phase, on soybean in the 5th trefoil phase and on sunflower in the inflorescence phase, eliminate zinc and manganese deficiency by foliar application of zinc salts (zinc sulfate ZnSO4 · 7H2O) and manganese salts (manganese sulfate МnSO4·5H2O). ) with a chelating agent (EDTA / Trilon B or OEDP).
Zinc deficiency can also be eliminated by spreading zinc sulfate (ZnSO4 · 7H2O) in the amount of: 50 kg / ha – on corn and soybeans; 20 kg / ha – on sunflower.
Write to us
and we will find an opportunity
for cooperation